Do AMD Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G processors have enough power in gaming to make you forget about GPU?
- arytechblog
- Apr 11, 2024
- 6 min read
Updated: Oct 9, 2024
This blog is an Amazon affiliate, which means that if you click on a paid link from this website that takes you to Amazon and you purchase a product, I will receive a small commission. You can find links to Amazon in the highlighted words.
We adore PCs outfitted with the latest and most high-performance components, running games at the highest possible FPS in 4K resolution. However, what do you do when your gaming budget doesn’t stretch beyond the price of a second-hand flagship phone?

AMD addresses this question and caters to budget-conscious gamers and casual players by introducing the 8000G Series. This series could serve as a solution for those seeking gaming experiences without shelling out substantial sums for hardware. We put the Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G processors to the test, and our conclusions are rather reserved.
The technical specifications of processors in the 8000 series: Ladies and gentlemen, in ascending numerical order, the latest players joining the red team are: Ryzen 7 8700G (octa-core) and Ryzen 5 8600G (hexa-core), recommended for gaming in 1080p at an accessible price. Additionally, we have Ryzen 5 8500G (hexa-core) and Ryzen 5 8300G (quad-core), suitable for less demanding office PCs, compact setups, or home use.
Model | Ryzen 3 8300G | Ryzen 5 8500G | ||
Cores / execution threads | 4 / 8 | 6 / 12 | 6 / 12 | 8/16 |
Boost Frequency/Base Frequency | 4.9GHz / 3.4GHz | 5.0GHz / 3.5GHz | 5.0GHz / 4.3GHz | 5.1GHz / 4.2GHz |
Total Cache | 12MB | 22MB | 22MB | 24MB |
TDP | 65W | 65W | 65W | 65W |
NPU | N/A | N/A | Da | Da |
Today, we’ll be diving into the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G, currently retailing at $329 and $179, respectively. These processors showcase AMD’s latest Zen 4 and RDNA 3 architectures, marking their first APU (Accelerated Processing Unit) update since 2021 when they introduced the acclaimed 5000G series. While APUs aren’t meant to compete with or replace dedicated graphics cards, they offer ample performance through their integrated GPUs.

The top performer of the 8000G series, namely the Ryzen 7 8700G, comes equipped with 8 cores, 16 threads, 24 MB of cache memory, and Radeon 780M graphics, all while maintaining a TDP of just 65W. Following closely behind, yet still formidable, is the Ryzen 5 8600G, offering 6 cores, 12 threads, 22 MB of cache memory, and Radeon 760M graphics.
Model CPU | ||
Model iGPU | Radeon 760M | Radeon 780M |
Architecture | RDNA 3 | RDNA 3 |
Pipelines | 512 | 768 |
TMUs | 32 | 48 |
ROPs | 16 | 32 |
Nuclee Raytracing | 8 | 12 |
iGPU frequency | 1500 – 2800 (Boost) MHz | 1500 – 3000 (Boost) MHz |
Power Consumption | 54W(35 – 54W TGP) | 54W(35 – 54W TGP) |
Monitors | maxim 4, HDMI 2.1, DP 2.1 | maxim 4, HDMI 2.1, Dp 2.1 |
The Radeon 780M integrated graphics processor within the chip is the most potent iGPU ever integrated into an APU, featuring 12 compute units (CUs). The graphics subsystem components are built on the RDNA 3 graphics architecture, initially utilized in the Radeon 7000 series of graphics cards. In the Ryzen 7 8700G, the Radeon 780M integrated graphics processor operates at a frequency of 2.9GHz, which is 100MHz faster than the identical Radeon 780M solution found in the laptop variant of the Ryzen 9 7940H.

Benchmark results for the Ryzen 7 8700G and 5 8600G APUs
Sure, besides the technical specifications, what capabilities do these new AMD processors offer? To uncover the answer, I conducted CPU and GPU tests, as well as played some games with settings set to Low. As mentioned earlier, I only had access to the two powerhouse processors in the lineup: the Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G. Let’s begin with the results from the synthetic tests:
Score (points) | Ryzen 5 7600 | Ryzen 7 7700 | ||
Cinebench R23 MC | 12872 | 17239 | 14288 | 18658 |
Cinebench R23 SC | 1675 | 1763 | 1844 | 1917 |
In Cinebench, we can clearly discern the positions of the two processors from the 8000 series. Consequently, the Ryzen 7 8700G falls slightly below the Ryzen 7 7700 (with a difference of 7-8%), while the Ryzen 5 8600G exhibits slightly weaker performance than the Ryzen 7600 (to be precise, by 10%). What accounts for these variances? It’s simple: the 7000 series boasts more cache memory. Now, let’s swiftly examine the graphics subsystem in synthetic tests:
Score (points) | AMD Ryzen 9 7950X | ||
Superposition 4K Optimized | 1995 | 2289 | 578 |
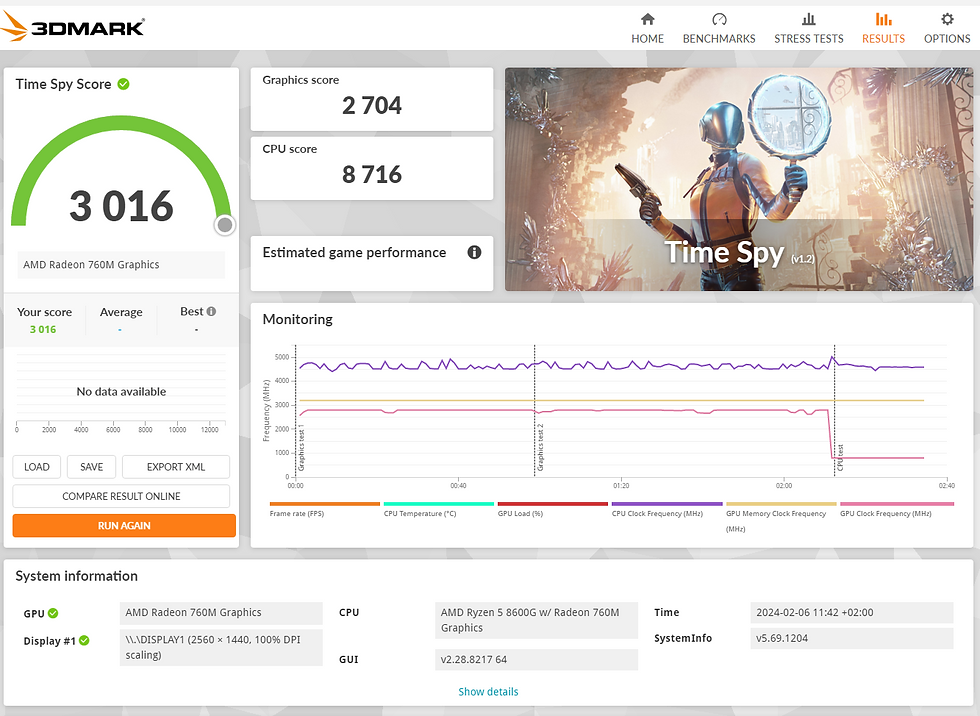
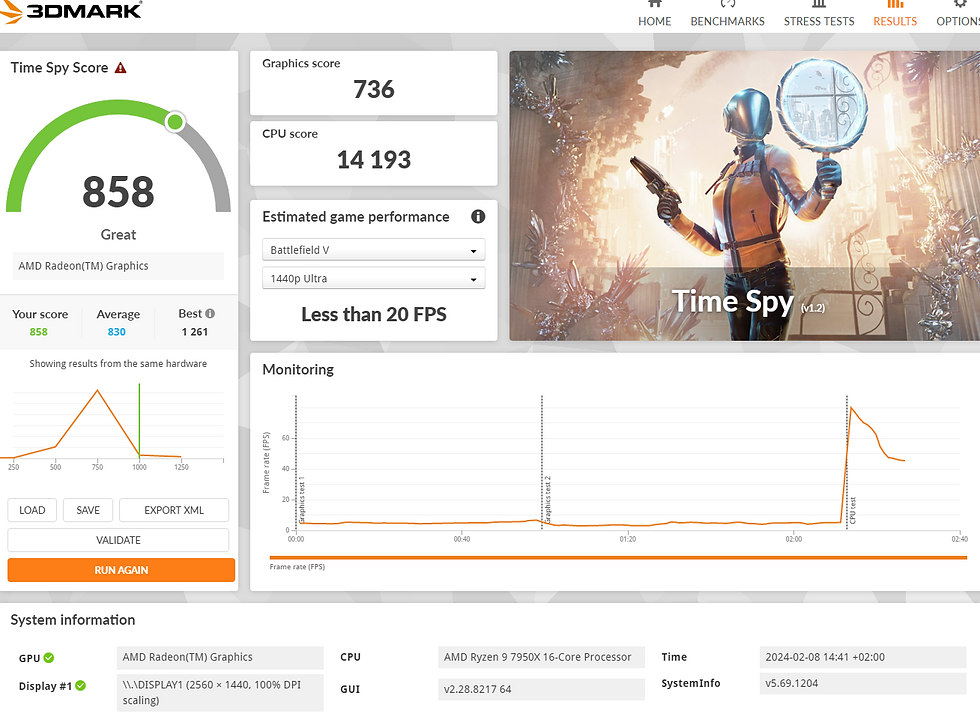
3DMark Time Spy | 3016 | 3602 | 858 |
Graphics | 2704 | 3208 | 736 |
CPU | 8716 | 11907 | 14193 |
3DMark Fire Strike | 7179 | 8176 | 2369 |
Graphics | 7789 | 8865 | 2519 |
Physics | 20152 | 24389 | 44314 |
Combined | 2812 | 3169 | 827 |
I’ve compiled the results from a Ryzen 7950X to illustrate the disparity between an APU’s integrated GPU and a standard CPU’s integrated GPU. The discrepancies are substantial, with the 8600G alone being 3-4 times more potent than the Radeon integrated into the 7950X.

But let’s face it, nobody’s eagerly anticipating the results of synthetic tests. We’re all eager to see how they perform in the real test: gaming. As I mentioned earlier, I put both processors to the test in Red Dead Redemption 2, Forza Horizon, GTA V, and DOTA 2, all set at 1080p resolution with Low settings across the board. I opted for games that are more forgiving on lower-end systems, as it’s evident that a title like Cyberpunk 2077 would be a slideshow on GPUs of this caliber.
Average FPS | ||
RDR2 1080p low | 47.09 | 48.48 |
Forza Horizon 1080p low | 54 | 71 |
DOTA 2 1080p low | 175 | 187 |
GTA V 1080p low | 124 | 130 |
The results are quite impressive, in my opinion. E-sports titles run smoothly on both the Ryzen 5 8600G and Ryzen 7 8700G, a feat not commonly achieved by other APUs. However, Red Dead Redemption 2 does present a challenge, with neither processor reaching close to 60FPS. Nevertheless, it’s important to remember that we’re dealing with integrated GPUs here. For perspective, the 7950X achieved an impressive 32 FPS in Forza Horizon.
For a performance boost, you can experiment with AMD’s Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) function. However, I recommend using a more robust cooler than the standard one if you intend to overclock the CPU (and GPU), which comes unlocked from the factory. This is because temperatures under full load can reach 79 degrees for the Ryzen 5 8600G and 91 degrees for the Ryzen 7 8700G. Nevertheless, I have two caveats here: first, you won’t typically encounter these temperatures under normal operation; and second, you should only be concerned if temperatures exceed 95 degrees, which they don’t in this case.
Who are the target users for these processors, though?
Up until now, it might seem like a budget-friendly gaming processor, but there are some hurdles to consider. To utilize Ryzen 8x00G, you’ll need an AM5 socket motherboard and DDR5 RAM, both of which come with a hefty price tag in the current market. While this setup is indeed “future-proof” and a solid choice, particularly if you’re constructing your PC from the ground up and plan to upgrade to a dedicated graphics card later on, the notion of it being a low-budget option sort of goes out the window.
It’s worth noting that the previous series, the Ryzen 5000G, continues to hold significance in the low-budget segment, especially following the introduction of the new lineup. The Ryzen 7 5700G, priced at $198, stands out as an exceptionally appealing option, particularly when paired with the affordable AMD AM4 motherboards and DDR4 memory. Furthermore, the Ryzen 5 5600G, priced even lower at $119, remains an excellent choice for users on a very tight budget, offering the capability to handle basic tasks and enjoy gaming at 720p resolution without requiring a dedicated graphics card.
However, the APUs of the 5000 series fall significantly short in performance compared to the 8000 series. While gaming at 1080p is perfectly feasible with the 8000 series, you often have to downgrade to 720p with the 5000 series. This is particularly noticeable in non-e-sports titles, where the disparities are substantial.
Another alternative to the 8000 series would be combining a low-end processor (such as the 14100f) with an equally low-end graphics card (like NVIDIA’s GTX1650, for example). However, this solution comes with its drawbacks: the resulting setup will be larger in size, consume more power, and a potential upgrade to the graphics card may leave you with a less than optimal processor.
In summary, the Ryzen 7 8700G delivers commendable performance for its price point. However, the overarching issue with the entire 8000 series is its positioning—too costly for budget-conscious users and lacking the horsepower for demanding gaming endeavors. This dilemma has persisted since the inception of APUs, and the 8000 series doesn’t mark a significant departure from this trend. Nonetheless, we’re edging closer to a turning point, with the Ryzen 7 8700G serving as a prime example of this evolution.
Both the Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G could serve as viable options for gamers who haven’t allocated funds for a dedicated graphics card or for users seeking to construct a more economical or ultra-compact system. In reality, I believe this is where the majority of the market for these processors will lie: within mini-ITX, SFF (small form factor) office, or gaming systems.
Having said that, I wish you a wonderful day and I look forward to reading the next article. For this you will have to subscribe to the newsletters.



Comments